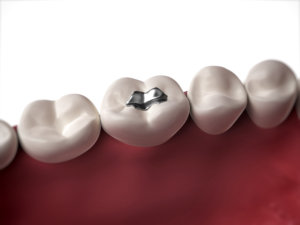
Amalgam fillings consist of more than 50% highly toxic mercury. In dentistry, this material has been highly controversial since its introduction at the beginning of the 19th century and was even temporarily banned in the USA. However, the use of this material has been able

1. From 1 January 2019, dental amalgam shall only be used in pre-dosed encapsulated form. The use of mercury in bulk form by dental practitioners shall be prohibited. 2. From 1 July 2018, dental amalgam shall not be used for dental treatment of deciduous teeth,

“Mercury naturally adheres to plastics in the water, by creating extremely concentrated “fish food” bombs of dangerous chemicals. Plastic has a negative charge, mercury has a positive charge. Opposites attract so the mercury sticks….”

EEB-WA-ECEM_Devel_Natl_Phase_Down_Plans_April_2019

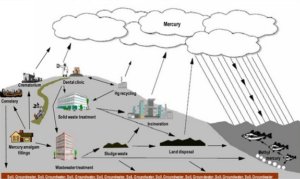
After amalgam is in circulation, it is difficult to control because it enters the environment via so many pathways. Additionally, it is often cost-prohibitive to capture all of these dental mercury releases. Before governments require costly amalgam waste management measures, the following points should be

The Minamata Convention on Mercury is a global treaty to protect human health and the environment from the adverse effects of mercury. The Convention requires each party to “phase down the use of dental amalgam.” It also addresses amalgam in Annex A, where it can
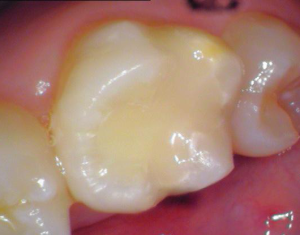
Mercury-free dental fillings have been developed and studied for over fifty years. As a result, a wide variety of dental restorative materials to meet all needs are available today. The most popular mercury-free fillings include: Composite Bulk-Fill Composites Glass ionomer Compomer Advantages of mercury-free fillings
Average tonnes of mercury consumed in products each year Between 270 and 341 tonnes of mercury are consumed globally for use in amalgam each year. Accounting for at least 10% of global mercury consumption, amalgam is among the largest consumer uses of mercury in the